Counting Without Running: Evaluating LLMs' Reasoning About Code Complexity
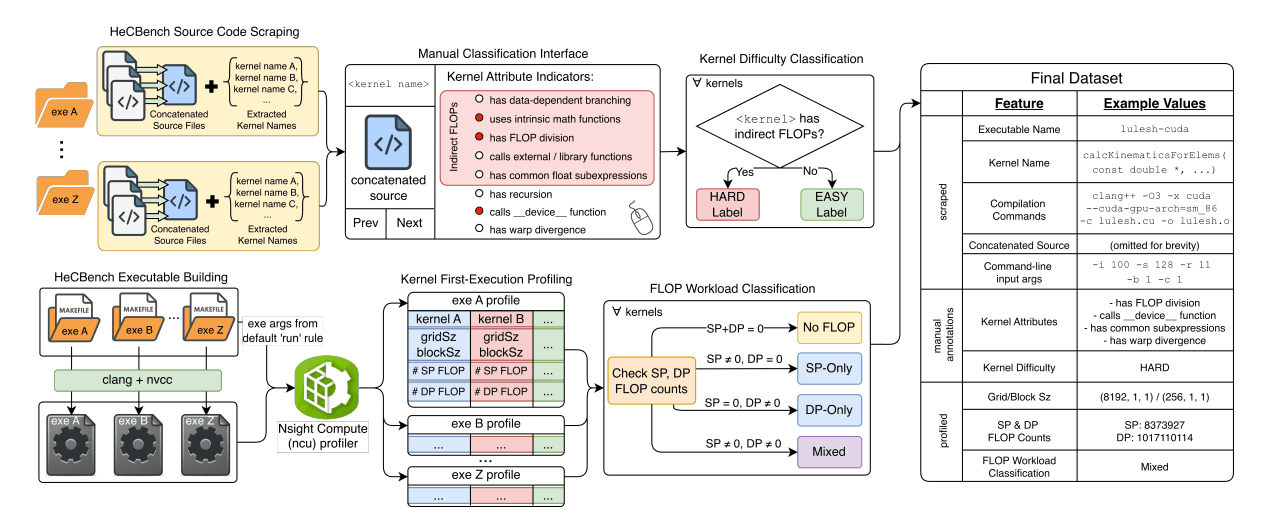
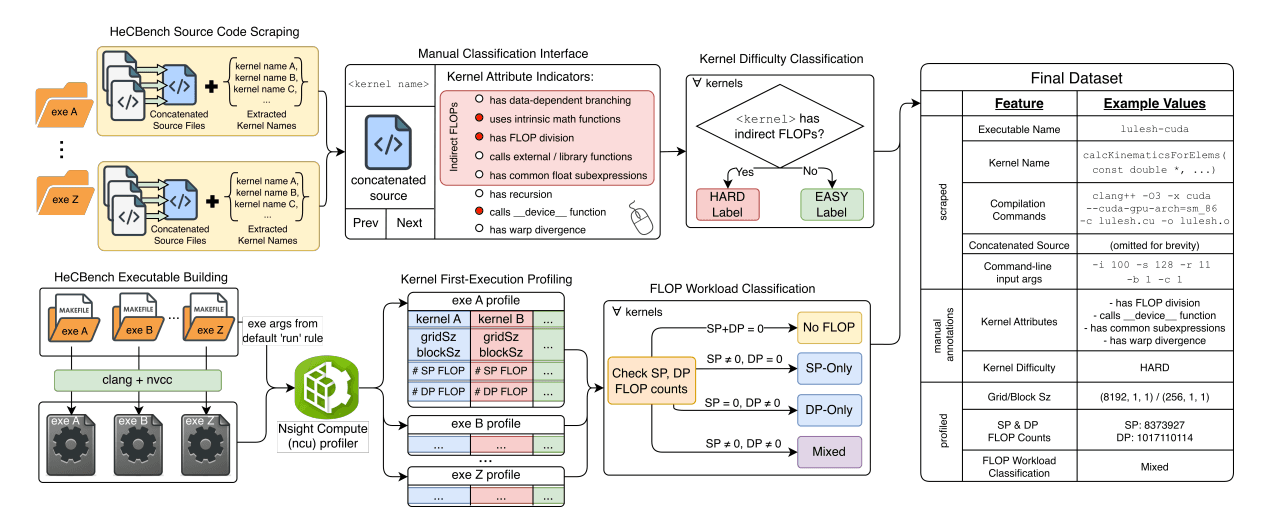
Introduces gpuFLOPBench, a benchmark containing 577 CUDA kernels to evaluate whether language models can predict floating-point operation counts without execution, revealing limitations in understanding hardware-specific performance details.
Abstract
This research introduces gpuFLOPBench, a benchmark containing 577 CUDA kernels designed to evaluate whether language models can predict floating-point operation counts without execution. The study reveals that modern LLMs handle straightforward kernels well but struggle significantly with complex scenarios involving division, math functions, or shared subexpressions—highlighting fundamental limitations in understanding hardware-specific performance details. These findings have important implications for using LLMs in performance optimization and code analysis tasks.
Related Research
UniPar: A Unified LLM-Based Framework for Parallel and Accelerated Code Translation in HPC
Introduces UniPar, an evaluation framework for assessing how large language models translate between parallel programming languages, achieving 69% compilation success and 33% functional correctness through fine-tuning and compiler-guided repair.
Workflows vs Agents for Code Translation
Compares structured workflows versus agentic approaches for MATLAB-to-HDL translation, showing that agentic methods with the Model Context Protocol increase simulation reach rates by over 20 percentage points on mid-sized models.